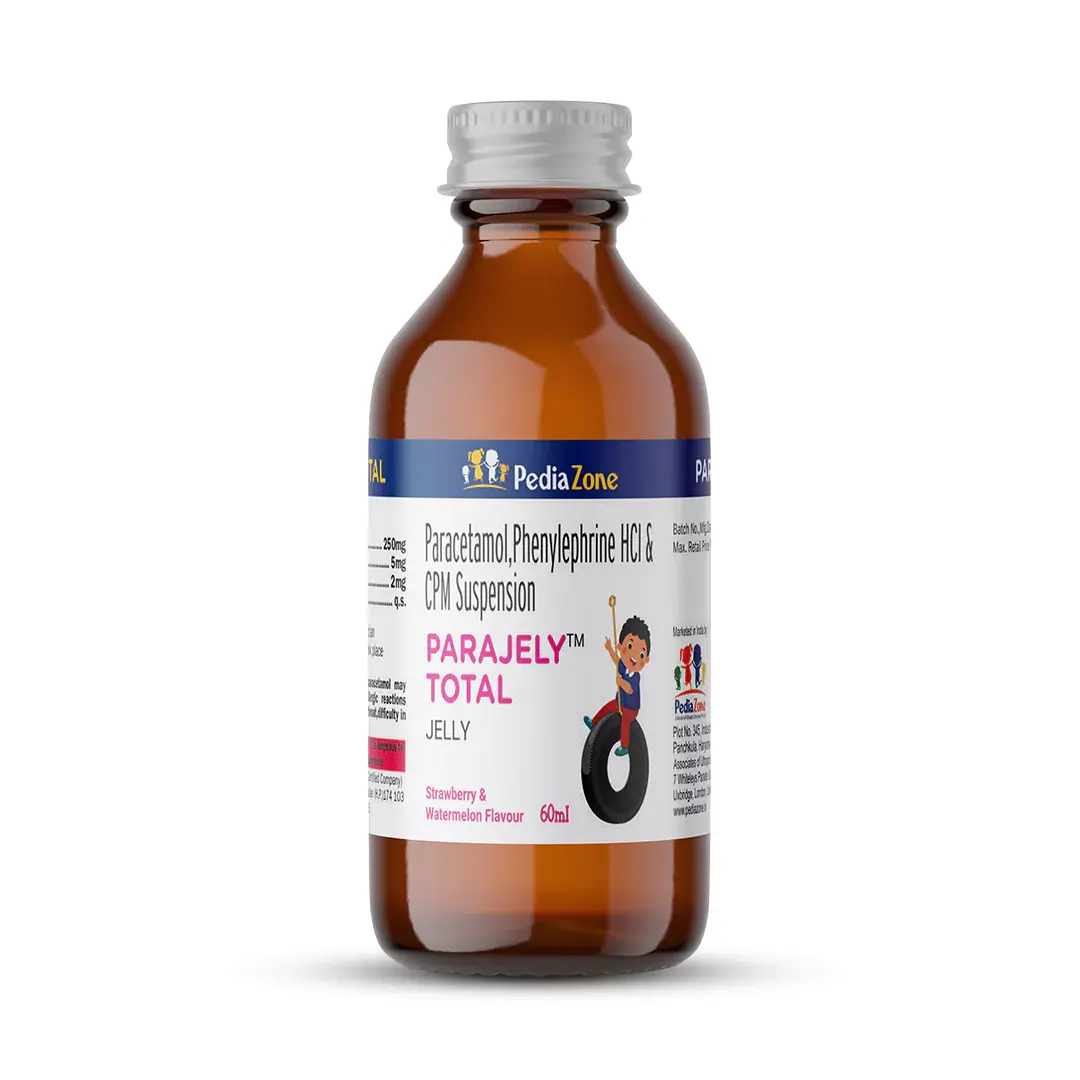
Therapy / Class: Antipyretic, Decongestant & Anti-Allergic (Cough & Cold Combinations) / Paracetamol: Para Aminophenol Derivatives + Phenylephrine: alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonist + Chlorpheniramine: Antihistamines
Mechanism of Action:
Paracetamol:
Analgesic Mechanism: It produces analgesic action by inhibiting the COX pathway in the central nervous system but not in peripheral tissues. It acts within the CNS to increase the pain threshold by inhibiting central cyclo-oxygenase (Both COX-1 & COX-2).
Anti-Pyretic Mechanism: It also produces antipyretic effect by inhibiting PG synthesis in the central nervous system & blocking the actions of endogenous pyrogens at the hypothalamic thermo-regulatory centres.
Phenylephrine: It possesses both direct and indirect sympathomimetic effects, primarily as a post-synaptic alpha-adrenergic agonist, producing potent vasoconstriction. This constriction of blood vessels leads to reduced blood flow to the nose, decreased amount of blood in the sinusoid vessels, and decreased mucosal edema, which relieves nasal congestion.
Chlorpheniramine: It is a H1-antagonists which compete with free histamine for binding at H1-receptor sites. Blockade of H1-receptors suppresses the formation of edema, flare, and pruritus that result from histaminic activity.
- Cough
- Fever
- Headache
- Mild Pain
- Rhinorrhea
- Sinus And Nasal Congestion
- Sneezing
- Sore Throat (Pharyngitis)
Dosage & Administration:
| Children of age between 2 to 12 years (body weight – 6-40 kg): The usual recommended dose is | ||
| Age in years | Weight in kg | Dose |
| 2–4 | 6–16.5 | 2.5ml TID |
| 4–9 | 16.5–28.6 | 5ml BID |
| 9–12 | 28.6–41.5 | 5ml TID |
References:
- BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13: 556.
- International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology | January 2019 | Vol 8 | Issue 1 Page 34
- CMAJ. 2014 Feb 18; 186(3): 190–199.